Get to know Nipah Virus, a zoonotic disease with a high fatality rate. Check the early symptoms, causes of spread from bats, and ways to protect yourself safely according to public health standards.
“Nipah Virus” has recently become a widely discussed and concerning topic on social media following reports of infections and deaths in India. Although there is no large outbreak in Thailand yet, the virus’s high fatality rate and severe symptoms, including encephalitis, make it important to understand this virus better. This knowledge will help us prepare and protect ourselves properly before it becomes too late.
Nipah Virus, or NiV, belongs to the same family as Hendra virus. It is a highly severe zoonotic disease first identified in 1998 during an outbreak among pig farmers in the village of Nipah, Malaysia, from which the virus gets its name.

The World Health Organization (WHO) classifies Nipah Virus as one of the "priority diseases" due to its potential to cause major outbreaks. Currently, there is no vaccine or specific treatment available for humans.
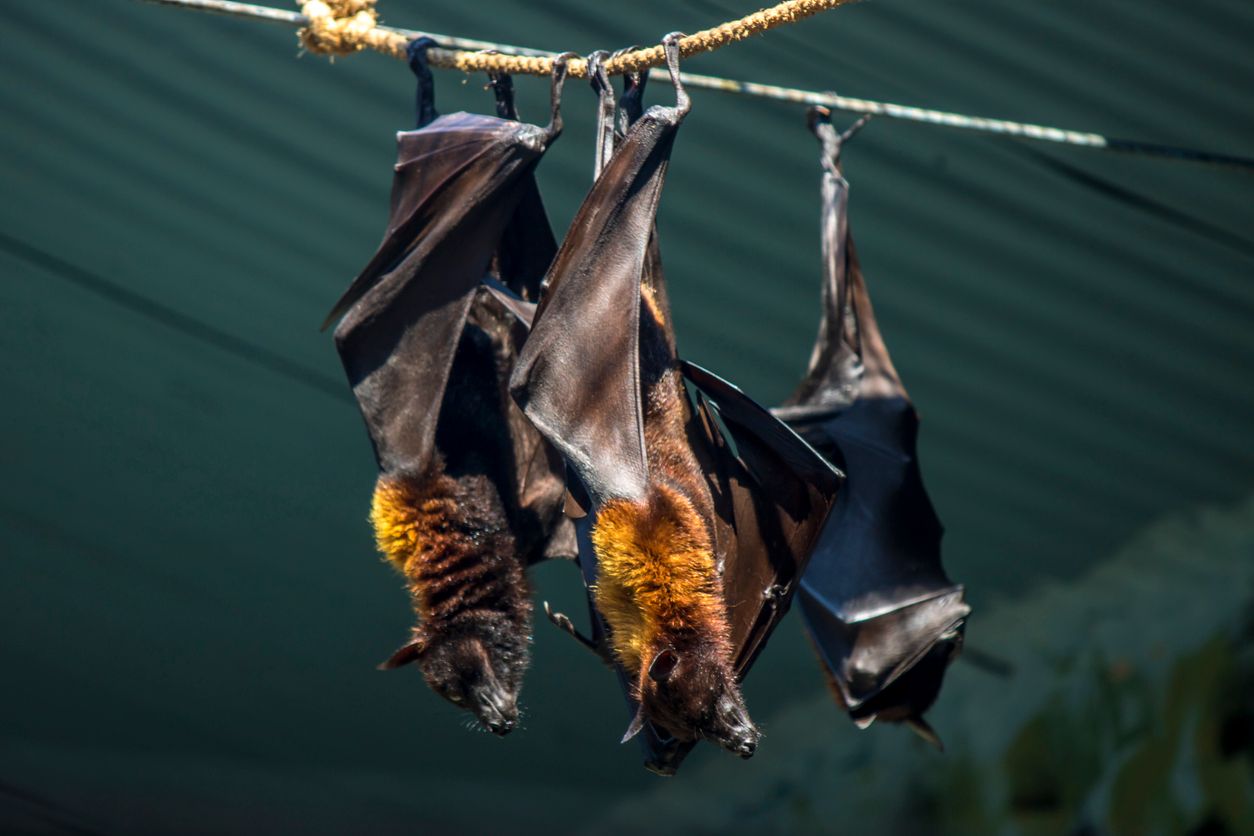
The natural carriers of Nipah Virus are fruit bats, especially the Pteropus genus. The virus lives in these bats without causing illness but can spread through their secretions such as saliva, urine, or feces.
The incubation period usually ranges from 4 to 14 days but can be as long as 45 days. Symptoms vary in severity as follows.
If the infection progresses, encephalitis (brain inflammation) can develop, with prominent symptoms including:
What alarms the world about Nipah Virus is its severity. Outbreak data from various areas show a case fatality rate between 40% and 75%, depending on the local medical capacity—significantly higher than COVID-19.
Currently, no vaccine exists for humans. The best prevention is reducing exposure to the virus.

Although there have been no human Nipah Virus cases reported in Thailand, the presence of Pteropus bats, natural carriers, has prompted continuous monitoring by the Ministry of Public Health. The most important advice is to remain vigilant: if you have a high fever along with a history of contact with animals or consuming suspicious fruit, seek medical attention promptly and provide detailed history.