Renal Denervation (RDN): A Technology to Treat High Blood Pressure Without Increasing Medication
- Treatment High Blood Pressure Treatment begins with lifestyle changes combined with doctor-prescribed blood pressure medication. However, many patients still cannot control their blood pressure, a condition known as resistant hypertension.
- Resistant hypertension is a condition where a patient’s blood pressure remains above target despite taking at least three types of blood pressure medications, including an appropriate dose of diuretics.
- Renal Denervation (RDN) is a procedure that uses modern technologyto treat the condition ofresistant hypertension. It can reduce systolic blood pressure by an average of 8–10 mmHg, with effects lasting more than 3 years.
High Blood Pressure (Hypertension) is a global health problem. According to the World Health Organization (WHO, 2023), over 1.28 billion people worldwide suffer from it, and the number continues to rise. This disease often shows no obvious symptoms early on and is therefore called"Silent Killer"because it can lead to serious complications such as heart attack, ischemic or hemorrhagic stroke,and chronic kidney failure.
What is Resistant Hypertension?
Generally, treatment for high blood pressure starts with lifestyle adjustments like diet control, exercise, and adequate rest, alongside prescribed medications. However, many patients still cannot control their blood pressure, a condition known as resistant hypertension. This condition is when a patient’sblood pressure remains highbeyond target levels despite taking at least three types of blood pressure medications, including an appropriate dose of diuretics.
Currently, a new effective option for these patients is Renal Denervation (RDN). This advanced technology reduces the activity of nerves controlling blood pressure by inhibiting the sympathetic nerves around the renal arteries, which stimulate blood vessel constriction and directly raise blood pressure.
The sympathetic nervous system plays a key role in blood pressure control. The renal sympathetic nerves send signals to various processes including:
- stimulating the kidneys to release renin, which activates the Renin–Angiotensin–Aldosterone System (RAAS), causing blood vessels to constrict and retain sodium and water.
- increasing sodium reabsorption in the kidney tubules, leading to higher blood volume in the body.
- directly triggering blood vessel constriction.
What is Renal Denervation (RDN)?
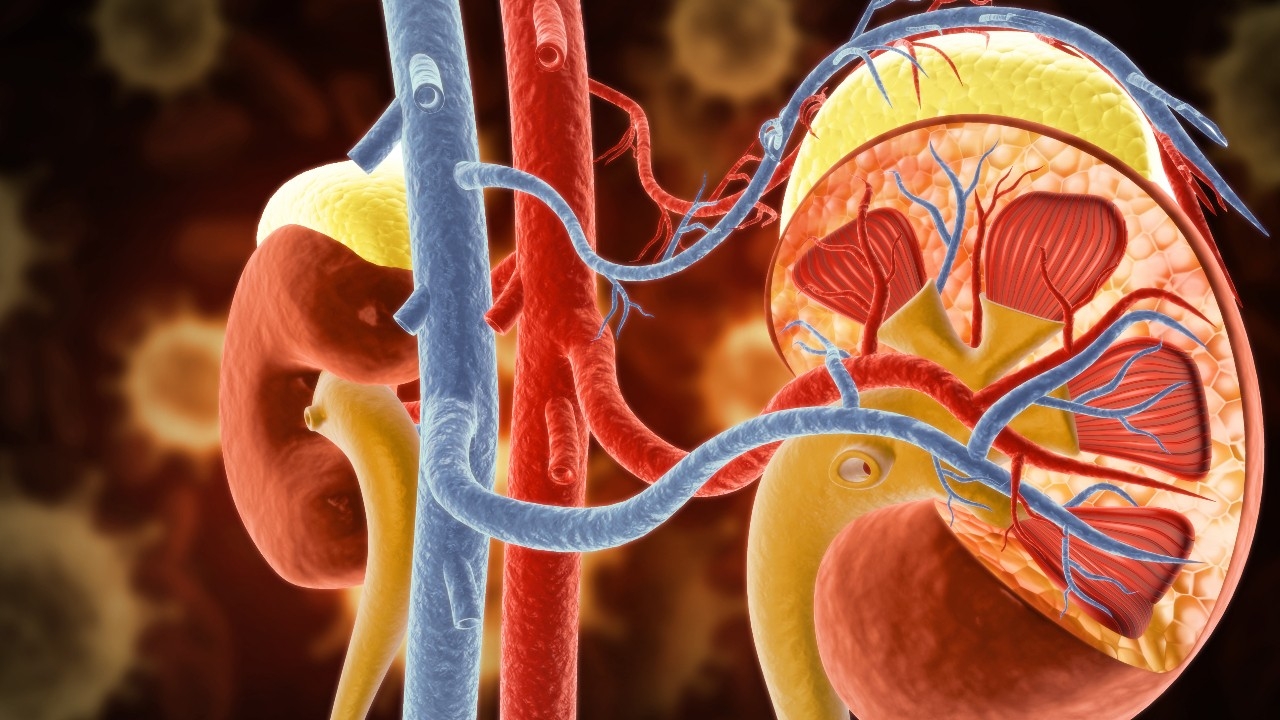
Renal Denervation (RDN) is a procedure using modern technologyto treat resistant hypertension. A physician inserts a catheterthrough a large artery in the groin areato reach the renal artery. Once in position, the doctor applies energy such as radiofrequency ablationor ultrasound energy.These energy forms destroy some of the nerves around the renal artery, which play a key role in blood pressure control. As a result, nerve signals between the brain and kidneys decrease, reducing the release of substances that raise blood pressure. This leads to a gradual and sustained blood pressure reduction.. (Image)
Overall physical evaluation
- 24-hour ambulatory blood pressure monitoring
- Assessment of kidney function and vascular condition
- 2. Procedure Steps
Local anesthesia or sedation is administered
- A catheter is inserted through the femoral artery in the thigh
- The catheter is advanced to the renal artery
- Energy is applied to ablate nerves around the arterial wall
- The procedure takes approximately 40–60 minutes
- 3. Post-procedure Care
The patient rests in the hospital overnight
- Monitoring for pain or complications such as bleeding or blood vessel blockage
- Continuous blood pressure monitoring
- Indications for RDN
According to guidelines from the European Society of Cardiology (ESC) 2023 and the American Heart Association (AHA), RDN may be considered for the following patients:
Patients with high blood pressure who take at least three medications including diuretics but still cannot control their blood pressure Patients who cannot tolerate medications or experience side effects Patients with persistently high blood pressure despite proper medication and treatment
- Those at high risk of complications such as heart failure, kidney failure, or stroke
- Research Results
- Key studies include
- the SYMPLICITY HTN-3 trial (2014, NEJM), a randomized controlled trial showing that RDN is safe but initially did not show significant blood pressure reduction compared to controls. However, later studies improved techniques and devices, showing better outcomes.
Reduces the need for multiple medications
Decreases risk of medication side effects
- Provides long-lasting results, maintaining blood pressure reduction for years
- Low risk and high safety
- Short treatment time
- Limitations of RDN
- Treatment evaluation depends on physician judgment. It is suitable for patients with hard-to-control blood pressure despite multiple medications.
- Results vary among individuals, with average reductions of about 8–10 mmHg; some may have more or less effect.
Medication is still needed because RDN complements rather than replaces blood pressure drugs.
- The procedure must be performed by specialized medical teams in hospitals equipped with appropriate technology and expertise.
- Renal Denervation (RDN)
- is a promising new option for effectively lowering blood pressure in patients with resistant hypertension or those wishing to reduce medication use. Although it is not yet a standard treatment for all patients, research shows clear potential in safety and long-term efficacy. However, treatment decisions should be made jointly with a physician, who will assess individual suitability.
- Information provided by Dr. Man Chantawimol, Cardiologist, Internal Medicine Department,
