Understanding Gallbladder Cancer: Symptoms, Risk Factors, and Prevention

Get to know gallbladder cancer, the disease Tony Jaa is fighting. Check initial symptoms, causes, who is at risk, and prevention guidelines based on medical standards.
It became news causing concern among fans worldwide when"Tony Jaa"or the world-renowned Thai action star Tony Jaa revealed his diagnosisof "gallbladder cancer,"a rare but highly aggressive form of cancer. We will explore this disease in detail—from early warning signs to prevention.
What is gallbladder cancer (Gallbladder Cancer)?
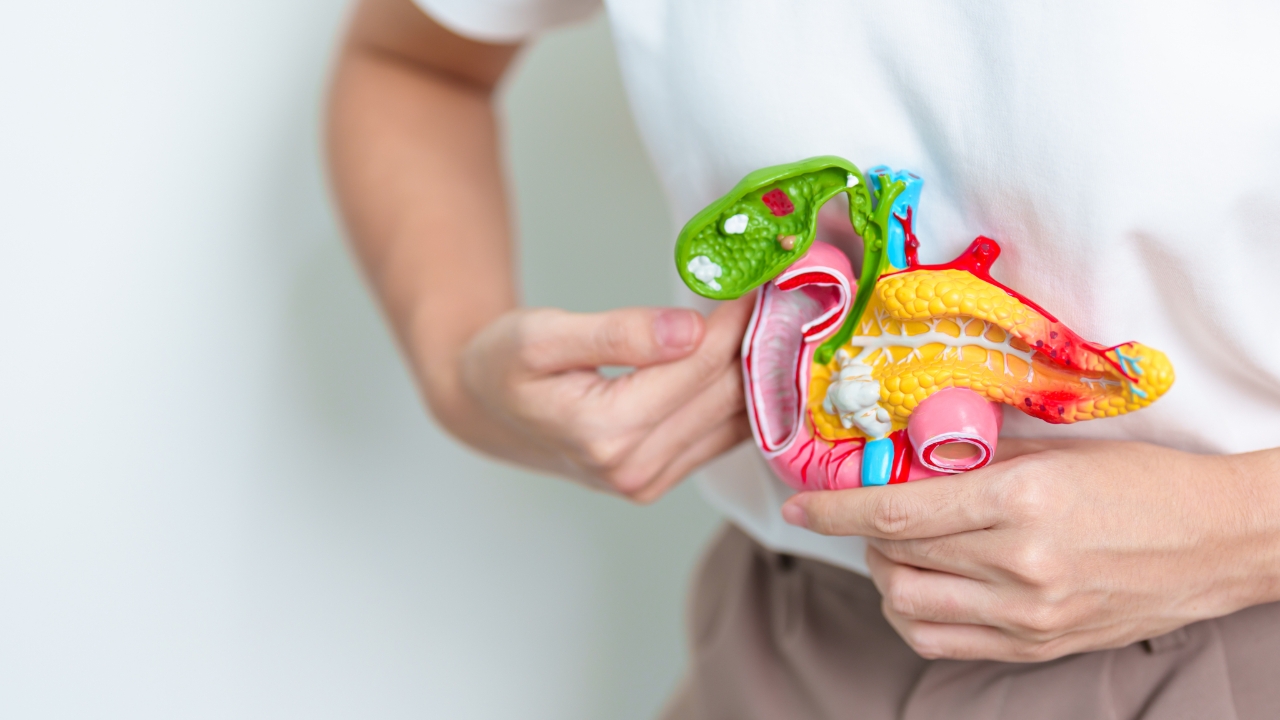
In the human body,the "gallbladder"functions as a reservoir that stores bile produced by the liver, releasing it to digest fats. Gallbladder cancer arises when cells in the gallbladder mutate and divide abnormally. The danger is that in early stages it often"shows no symptoms,"so most patients are diagnosed only after the cancer has spread.
Five stages of early warning signs of gallbladder cancer
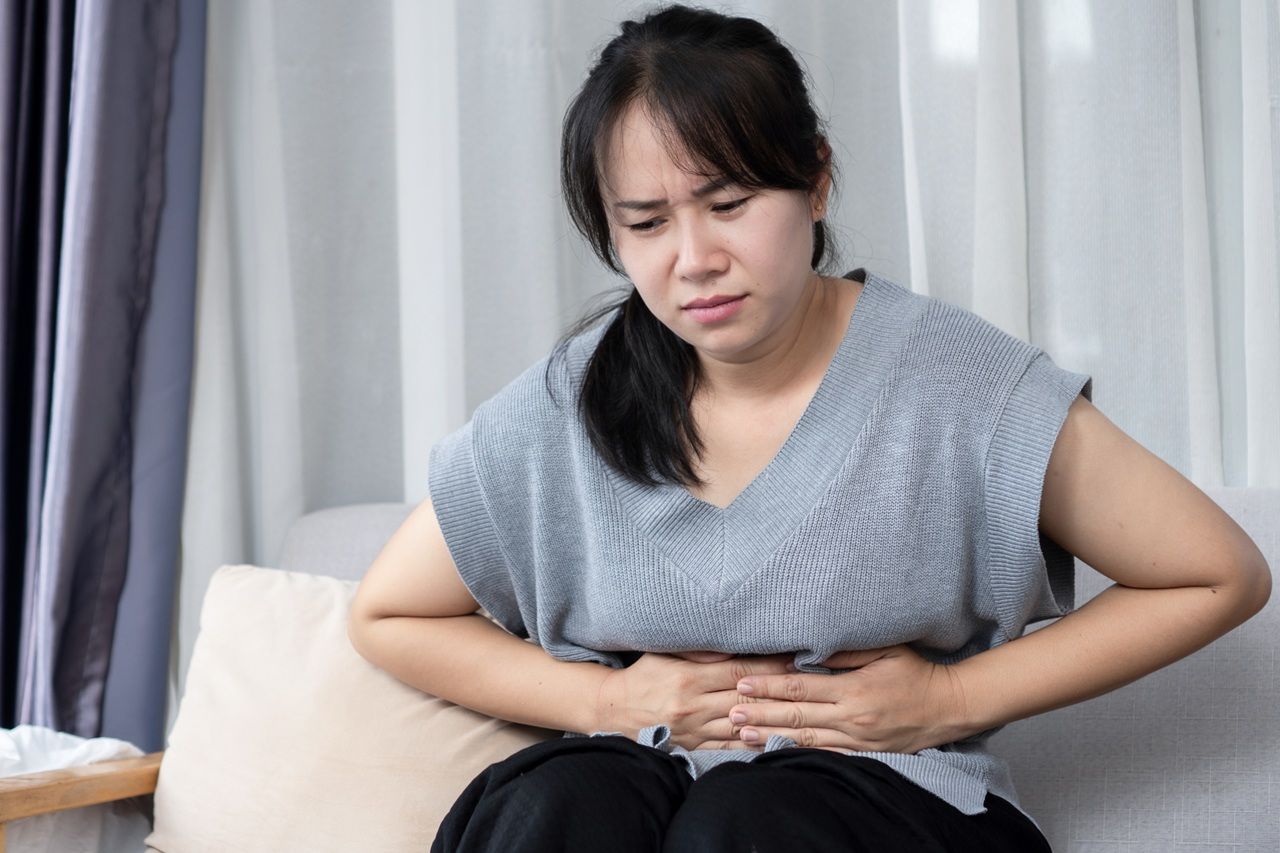
Typically, this cancer shows almost no symptoms early on. But when tumors grow or block bile ducts, the body starts to signal as follows:
- Abdominal pain with unclear location: usually starting as discomfort in the upper middle abdomen or right rib area, sometimes radiating to the back or right shoulder blade.
- Jaundice: the most distinct sign, occurring when tumors block bile ducts causing bilirubin to accumulate in the blood, turning the whites of the eyes and skin yellow.
- Changes in excretion: dark urine resembling strong tea and pale stools due to bile not reaching the intestines.
- Digestive disturbances: severe bloating, nausea, and vomiting, especially after eating fatty foods.
- General cancer symptoms: loss of appetite, unexplained rapid weight loss, and persistent low-grade fever.
Risk factors for gallbladder cancer: who should be especially cautious?
Gallbladder cancer does not have a single cause; it results from multiple factors leading to chronic inflammation of the gallbladder wall, eventually causing malignancy. The risk groups can be classified as follows:
1. Physical and biological factors
These are inherent or naturally occurring factors, difficult to control.
- Gender and hormones: statistics show that"women"are 3-4 times more likely to develop this cancer than men. Scientists believe"estrogen"plays a key role by stimulating the liver to produce more cholesterol in bile, leading to stones and inflammation.
- Older age: mostly found in people aged 60-70 and above, although cases are increasingly seen in younger people due to lifestyle changes.
- Congenital abnormalities: such as those with biliary cysts or abnormal connections between bile ducts and pancreas, causing pancreatic enzymes to reflux and chronically inflame the gallbladder.
2. Pre-existing medical conditions that act as"triggers"
If you have any of these chronic illnesses, you need close monitoring.
- Gallstones: individuals with stones larger than 3 cm have a much higher risk because stones constantly irritate the gallbladder wall causing ulcers and mutations.
- Gallbladder polyps: most are benign, but if a polyp islarger than1 cm, doctors usually recommend immediate removal due to a high chance of cancerous transformation.
- Porcelain gallbladder: a condition where calcium deposits harden the gallbladder wall like ceramic, resulting from long-standing inflammation.
- Chronic infections: such as being a carrier of typhoid bacteria or liver fluke infections, common in Asia including Thailand.
3. Behavioral and environmental factors
These are often overlooked by working-age people or those who appear outwardly healthy.
- Obesity: excess weight directly affects bile balance and increases the risk of gallstones.
- Diet and carcinogens: continuous consumption of high-fat foods or exposure to certain chemicals like nitrosamines found in fermented foods or some freshwater raw fish, and smoking.
- Family history: if a direct relative had gallbladder cancer, your risk doubles. Although not a primary cause, it requires vigilance.
How to prevent gallbladder cancer: lifestyle adjustments to reduce cancer triggers
Although no vaccine exists as for some cancers, maintaining"bile health"is the most crucial factor.
1. Maintain a healthy weight within standard limits
Obesity is a top risk factor because it raises cholesterol levels in bile, leading to stones and chronic inflammation.
- Caution: lose weight gradually. Rapid weight loss, such as severe dieting, can cause the liver to release excess cholesterol, increasing gallstone risk.
2. Choose high-fiber foods
- Focus on fiber: vegetables, fruits, and whole grains improve bile function and bowel health.
- Reduce bad fats: avoid foods high in trans fats, fried foods, or fatty meats that overwork the gallbladder.
- Good fats: eating omega-3-rich fish helps balance bile.
3. Don't let"gallstones"become chronic
If gallstones are detected, even without pain, consult a surgeon to assess risk. Large stones (over 3 cm) or multiple stones may require surgery to prevent future cancerous changes.
4. Avoid risky behaviors and contaminants
- Quit smoking: toxins in cigarettes increase cancer risk, including gallbladder cancer.
- Beware of liver fluke infections: avoid eating raw or undercooked freshwater fish dishes, such as koi pla, as parasites cause chronic bile system inflammation.
5. Proactive health screening
Since this cancer shows no early symptoms, general exams may be insufficient.
- Abdominal ultrasound: the simplest and safest method to detect stones, polyps, or gallbladder wall abnormalities.
- High-risk groups: those with a family history of gallbladder cancer should consult doctors for earlier and more detailed screening.
Why are healthy individuals at risk?
For apparently healthy people like athletes or action stars, risks may come from hidden factors such as asymptomatic gallstones or congenital bile duct abnormalities. Therefore,"upper abdominal ultrasound screening"during annual health checks is the only way to detect these abnormalities before it's too late.