
When income rises, especially for those with multiple sources such as salary, freelance work, rent, or independent professional income, a common question is: “How much additional tax must I pay, and which tax calculation method is most beneficial?”
This article by Thairath Money compiles and organizes information from official sources to help readers understand and practically apply tax filing, covering basic tax calculations and the key decision point between using the progressive method or the flat 0.5% method.
For personal income tax calculation, the basic formula is:
Tax payable = Net income × Tax rate
Where “net income” means total income throughout the year minus expenses and deductions allowed by law.
Net income = Total yearly income – Expenses – Deductions
This net income figure is then used to calculate tax by two methods, which taxpayers must compare.

The Revenue Department stipulates two main methods for personal income tax calculation:
The key rule is to calculate tax both ways and file using the method with the "higher tax payable" because these two methods use different tax bases.
The law requires comparing both methods and choosing the one with the higher tax to prevent cases where high income is offset by large deductions, resulting in abnormally low net income and tax that doesn't reflect actual earnings.
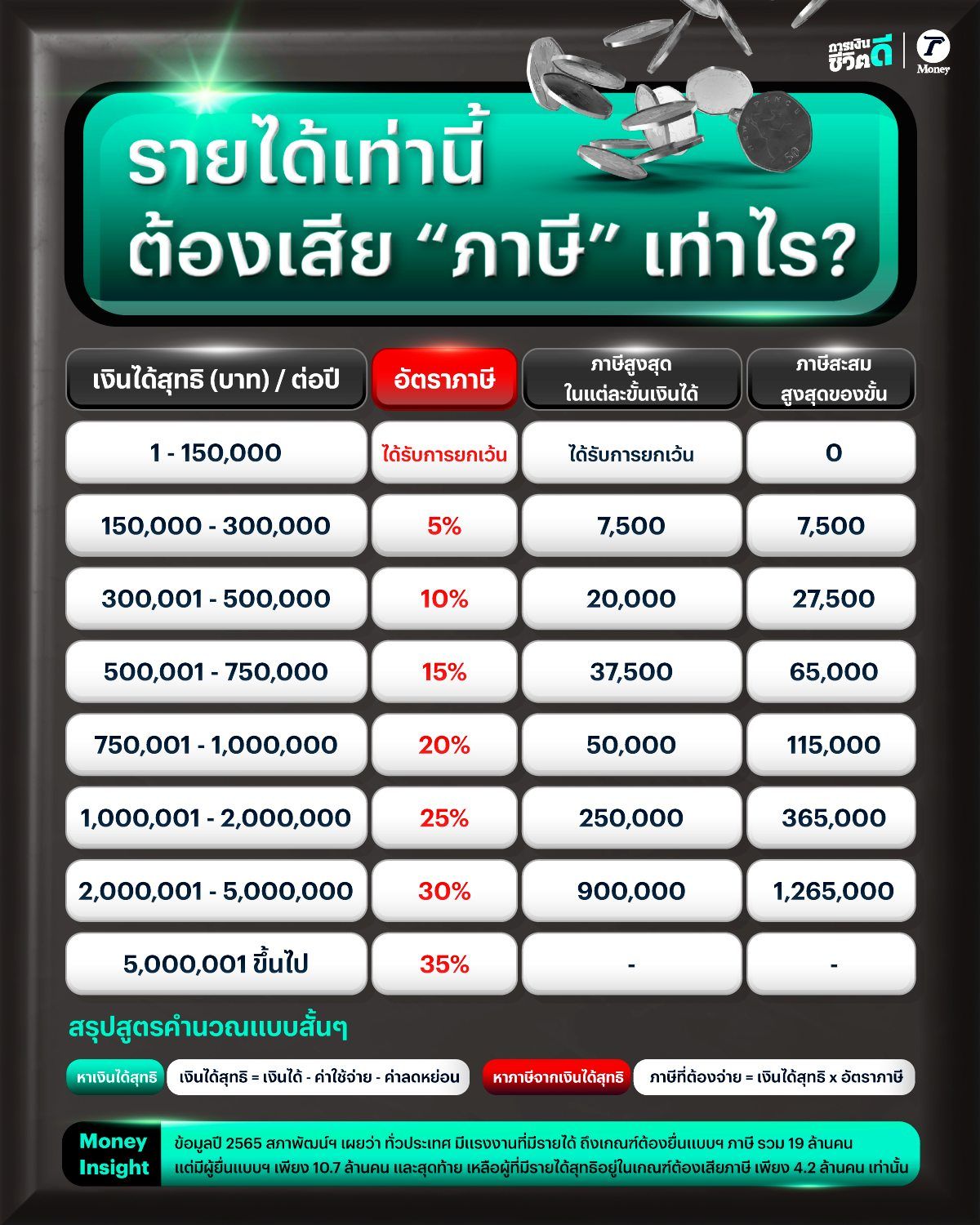
Progressive tax calculation is familiar to most people, especially salaried employees. The principle is that as net income increases, the tax rate increases in brackets. Once “net income” is determined, it is compared to personal income tax rates divided into brackets such as:
Advantages of the progressive tax method.
Cautions.
The flat 0.5% tax applies when you have income other than salary, such as freelance work, rent, independent professional income, and
The formula: Flat tax = (all income types except salary) × 0.005
Simply put, 5,000 baht tax per 1 million baht of other income.
Cautions for the flat tax method.
After calculating both methods, the Revenue Department’s online system will automatically do the comparison. Taxpayers don’t choose manually. As stated, the method resulting in higher tax must be used for filing.
Example 1: High income but using flat expense deduction.
An independent professional earns 1,200,000 baht and opts for flat expense deduction with a personal allowance.
Result: Must file using the progressive method because tax is higher.
Example 2: Very high actual expenses.
The taxpayer has the same income but claims large actual expenses.
Result: Must file using the flat tax method.
There is no definitive answer; it depends on individual income structure, expenses, and deductions.
The most important thing is to understand the system and fill in all information accurately. Ultimately, the system will select the correct method. Tax planning now not only helps reduce tax but also lets you manage increased income confidently without issues during next year’s tax filing.
Sources: Revenue Department, Krungsri Bank, edge by KKP.
Read personal finance news and financial planning with Thairath Money to achieve "Good finances, good life".https://www.thairath.co.th/money/personal_finance
Follow the Facebook page: Thairath Money at this linkhttps://www.facebook.com/ThairathMoney