
Microsoft announced the launch of the "Maia 200" officially its second self-developed AI chip, marking a long-term strategy to control AI infrastructure and reduce dependence on Nvidia hardware amidst the intense chip market competition, ongoing shortages, and rising costs.
The Maia 200, a new AI inference accelerator chip designed for large-scale AI inference tasks, will begin deployment this week at the company’s data center in Iowa, with plans to expand to Arizona next.
This move comes as leading cloud providers worldwide—including Microsoft, Google, and Amazon Web Services (AWS)—who are major Nvidia customers, are rushing to develop their own AI chips to mitigate supply constraints and achieve cost advantages amid soaring demand for AI processing power.
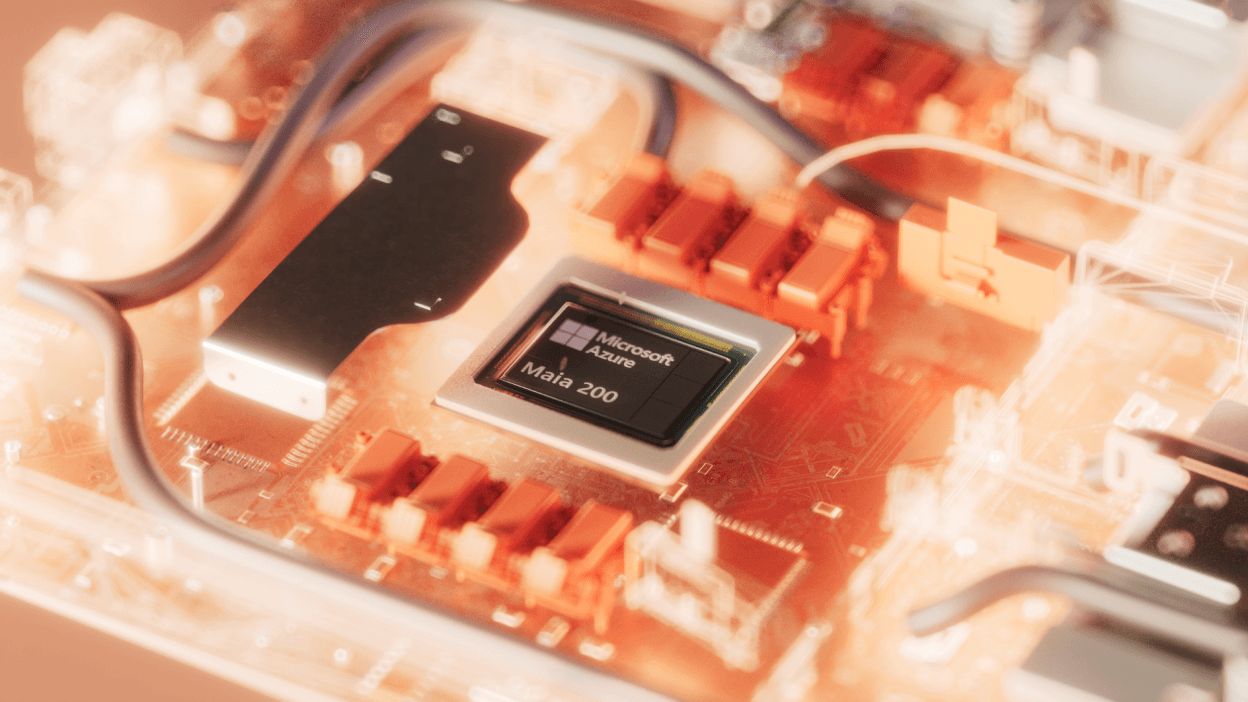
Microsoft revealed that Maia 200 is produced using TSMC’s 3-nanometer process, containing over 100 billion transistors, specifically designed as an AI accelerator for cloud workloads.
The company stated that Maia 200 delivers over 10 PetaFLOPS of 4-bit (FP4) processing and approximately 5 PetaFLOPS of 8-bit (FP8) performance, enabling rapid execution of complex AI models and future scalability, offering three times the performance of Amazon Trainium 3 and higher FP8 efficiency than Google’s TPU version 7.
Microsoft also described Maia 200 as "the most efficient inference system" it has ever deployed, engineered to handle numerous simultaneous user requests by incorporating a large amount of SRAM memory to accelerate AI system responsiveness.
These figures indicate that Microsoft positions Maia 200 not merely as an alternative to Nvidia chips but as a serious competitor in the cloud market, especially for inference workloads which are critical for commercial AI services such as chatbots and intelligent assistants.
Beyond hardware, Microsoft is making a significant software push by launching a development toolkit for programming the Maia 200 chip, which includes "Triton" an open-source software project co-developed by OpenAI, creator of ChatGPT. Triton is designed to perform similarly to Nvidia’s Cuda software, which industry analysts consider one of Nvidia’s key competitive advantages and a reason many developers remain tied to Nvidia’s ecosystem.
By promoting Triton alongside Maia 200, Microsoft demonstrates its ambition not only to own the chip hardware but also to build a comprehensive AI ecosystem—from silicon chip design and system software to cloud services and AI models integrated with data centers—creating a fully integrated platform.

Microsoft stated that Maia 200 will be utilized in the company’s primary services, including Copilot for business sectors and various AI models offered to customers via the Azure platform, including the latest models from OpenAI.
Some of the first chip batches will be used by Microsoft’s Superintelligence team to generate data for developing next-generation AI models. Meanwhile, the company has begun developing the next iteration, "Maia 300," and holds strategic options through collaboration with OpenAI to access new AI chip designs if necessary.
Analysts view the Maia 200 launch as a clear signal that Microsoft is making a long-term bet on the AI infrastructure battle amid global energy and chip supply constraints, where competition now hinges not only on "who has the best AI models" but also on "who controls costs and efficiency most effectively going forward."
Source of information Microsoft
Follow the Facebook page: Thairath Money at this link -