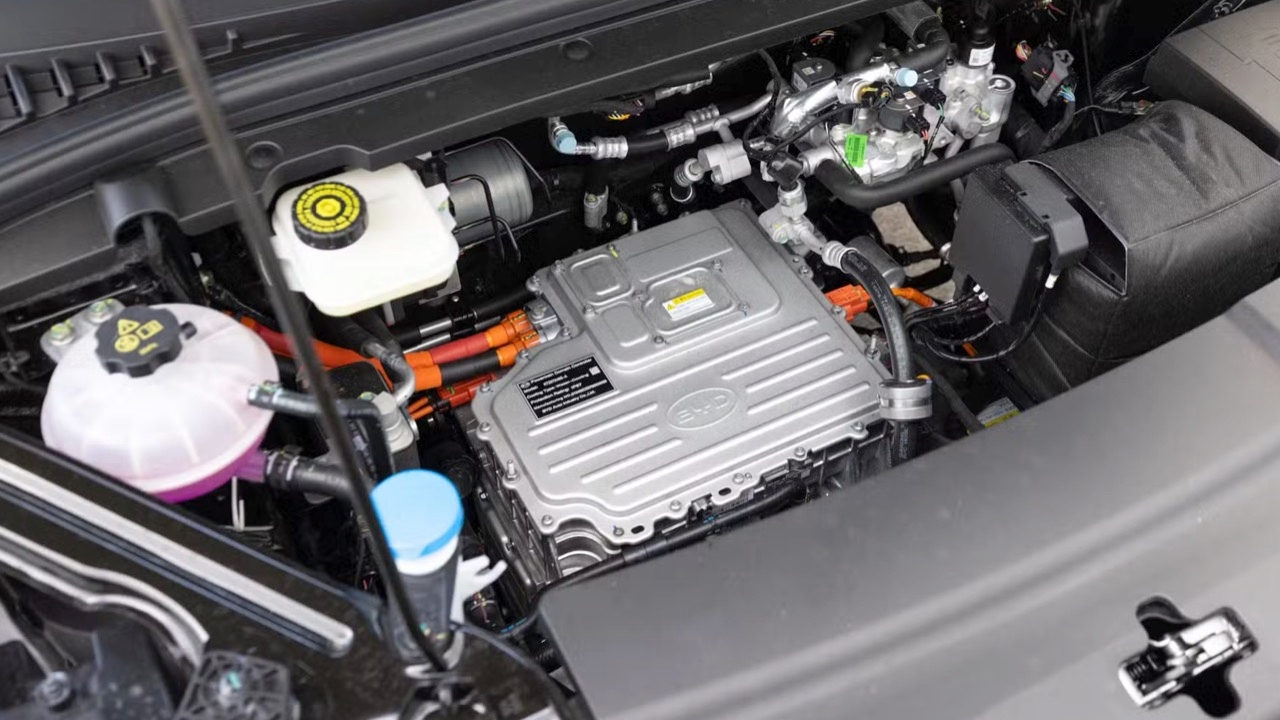

The cooling system of an electric vehicle (EV) serves the same purpose as that in an internal combustion engine car. However, instead of maintaining optimal temperatures for the engine and transmission, the EV cooling system maintains the temperature of the battery and drive motor to prevent overheating. Typically, batteries operate efficiently within a temperature range of 27 to 40 degrees Celsius. This temperature control is crucial for the battery, motor, and power electronics to ensure safety, performance, and longevity.
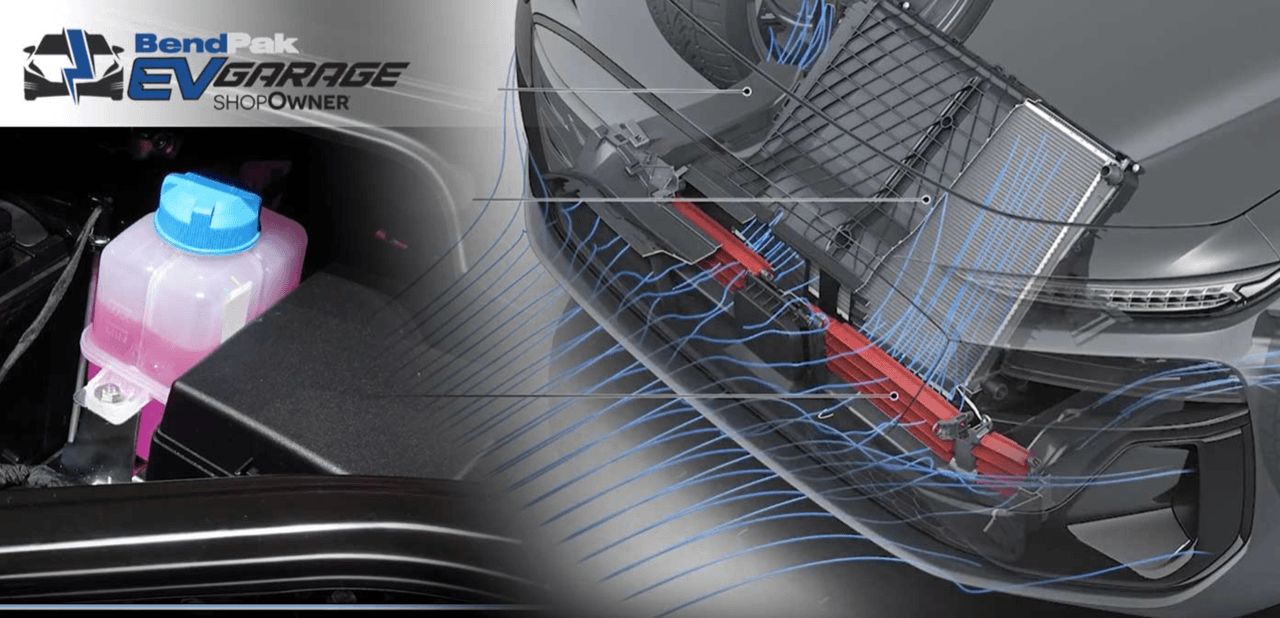


Liquid cooling is the primary method used, employing a mixture of water and glycol in cooling plates to effectively dissipate heat. Advanced EV cooling systems in some models utilize refrigerant cooling, heat pumps, and integration with the cabin air conditioning system to manage heat in critical electric drive components. Active or passive liquid cooling involves coolant flowing through pipes, jackets, or cooling plates to absorb heat from battery cells, motors, and inverters.
Air cooling is a simpler but less efficient method, using fans and ambient air to disperse heat. It is mostly employed in smaller electric vehicles or hybrids.
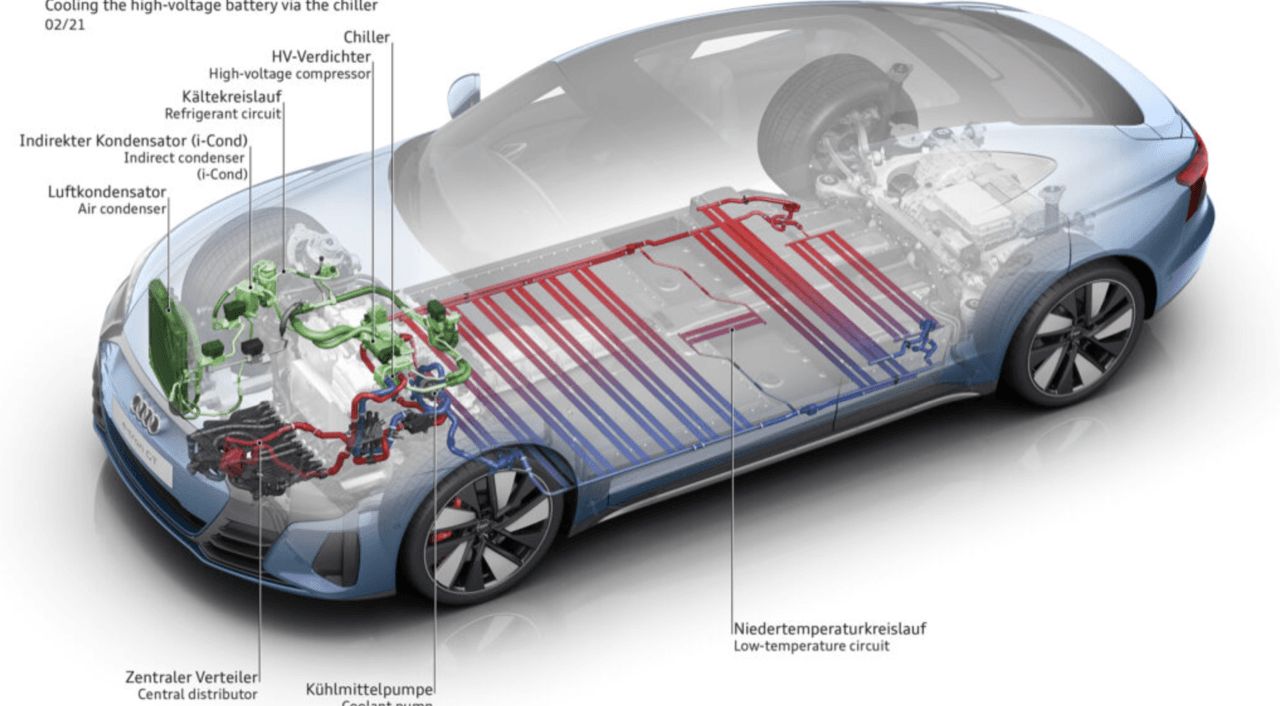
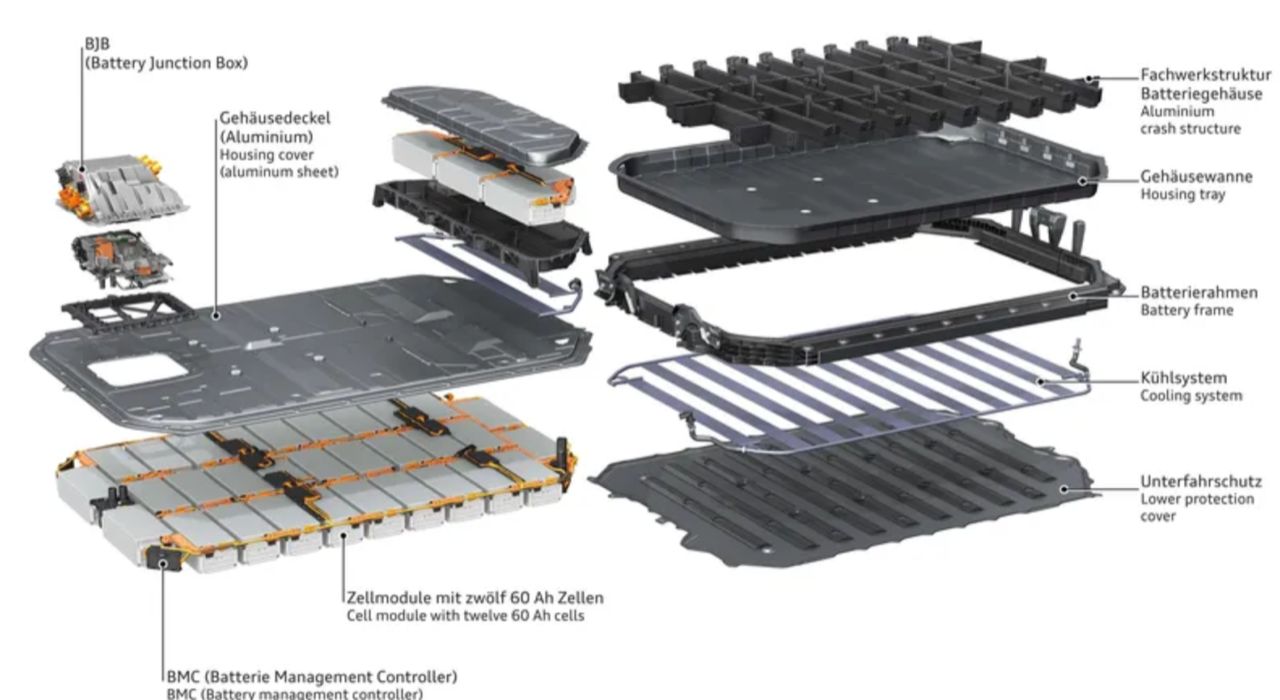
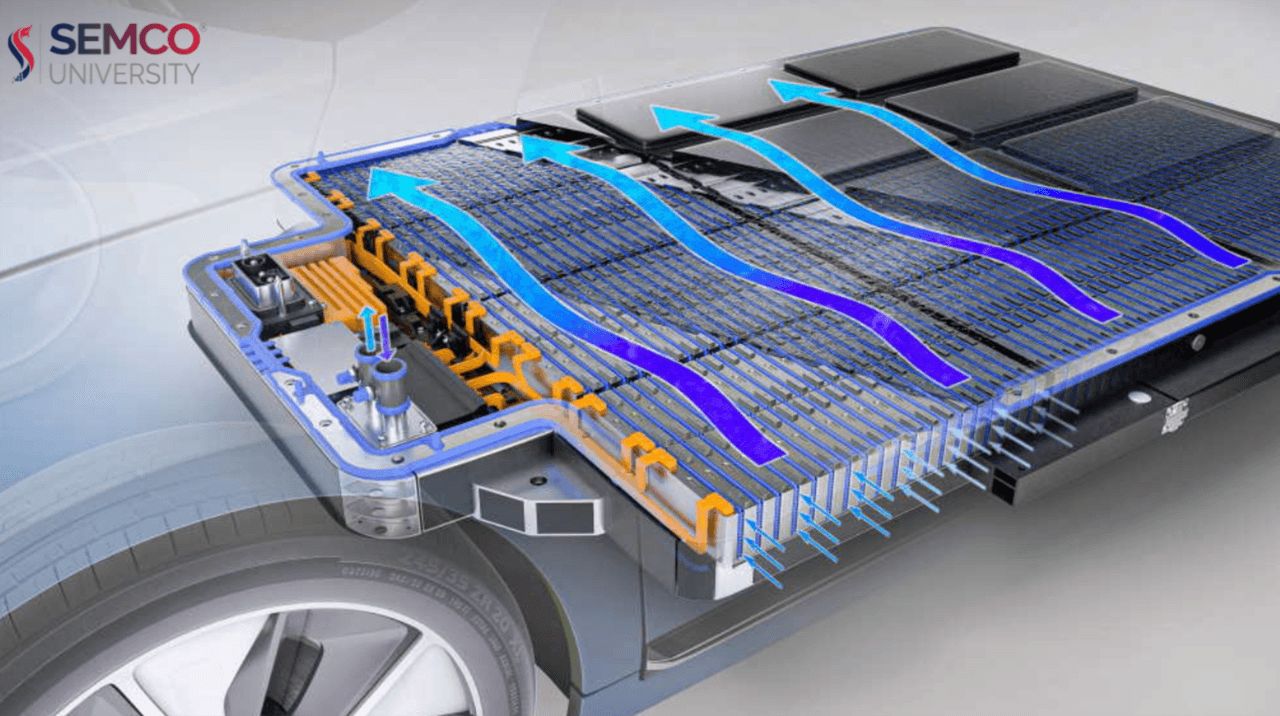
Refrigerant cooling / active cooling systems
This highly efficient heat transfer method connects the battery cooling circuit to the vehicle's air conditioning system (refrigerant circuit) for advanced cooling. Phase Change Materials (PCM) absorb significant heat during their transition from solid to liquid, enabling high-density thermal management. The primary role of this system is Battery Thermal Management System (BTMS), preventing excessive heat during fast DC charging and high-load or sustained high-speed driving, such as on race tracks. The cooling system also warms the battery in cold conditions; however, in Thailand, the battery heating function is rarely used due to the tropical climate, with cold temperatures only occurring for 1-2 months at night in highland areas. Even in winter daytime, strong sunlight can raise temperatures to 34-36 degrees Celsius, so battery warming is generally unnecessary.
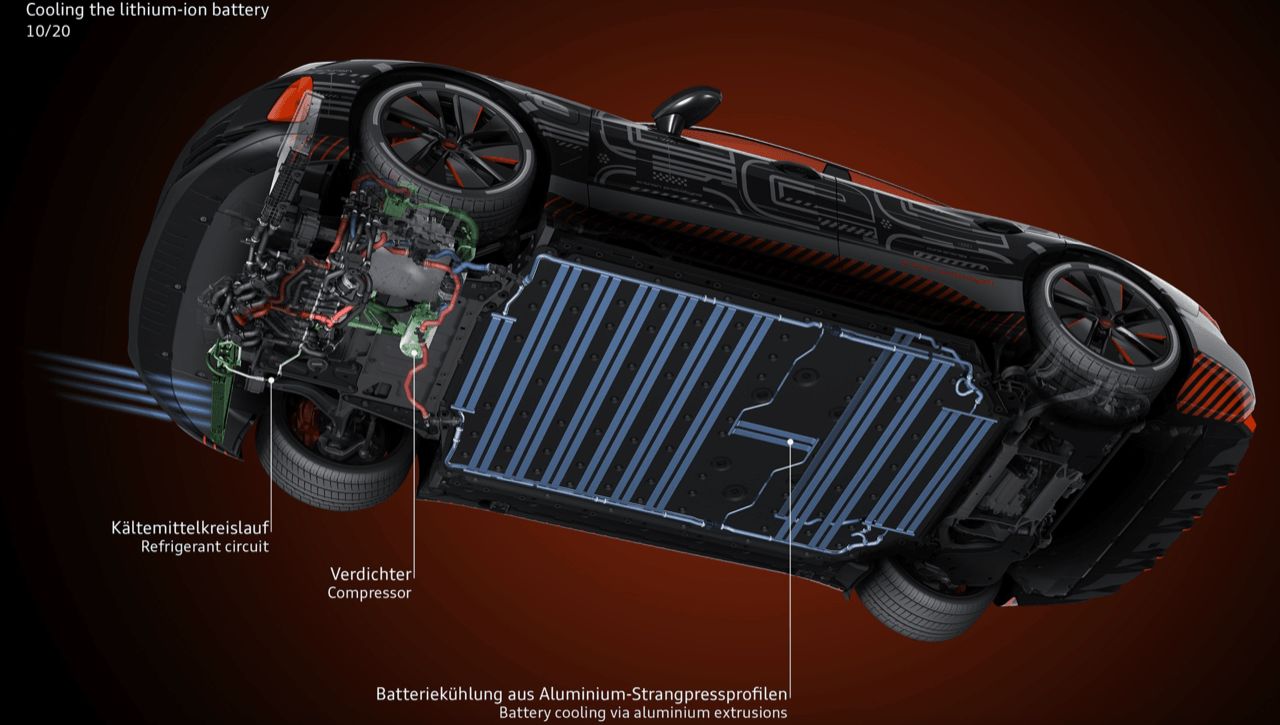

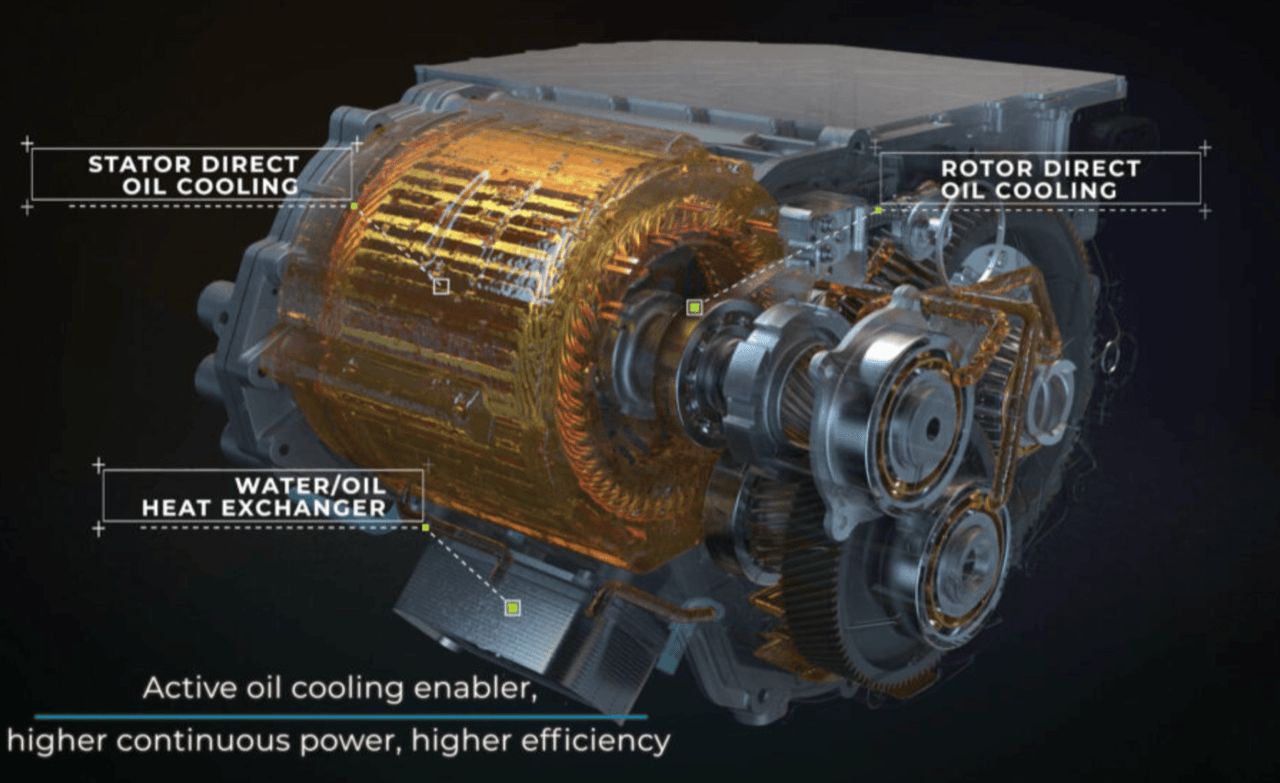
The EV cooling system also cools power electronics and motors to extend their lifespan and prevent excessive motor temperature. Components that conduct electric current and generate heat, such as inverters (using SiC MOSFETs or Si IGBTs) and electric motors, are usually cooled by liquid-cooling pipes to reduce system temperature.
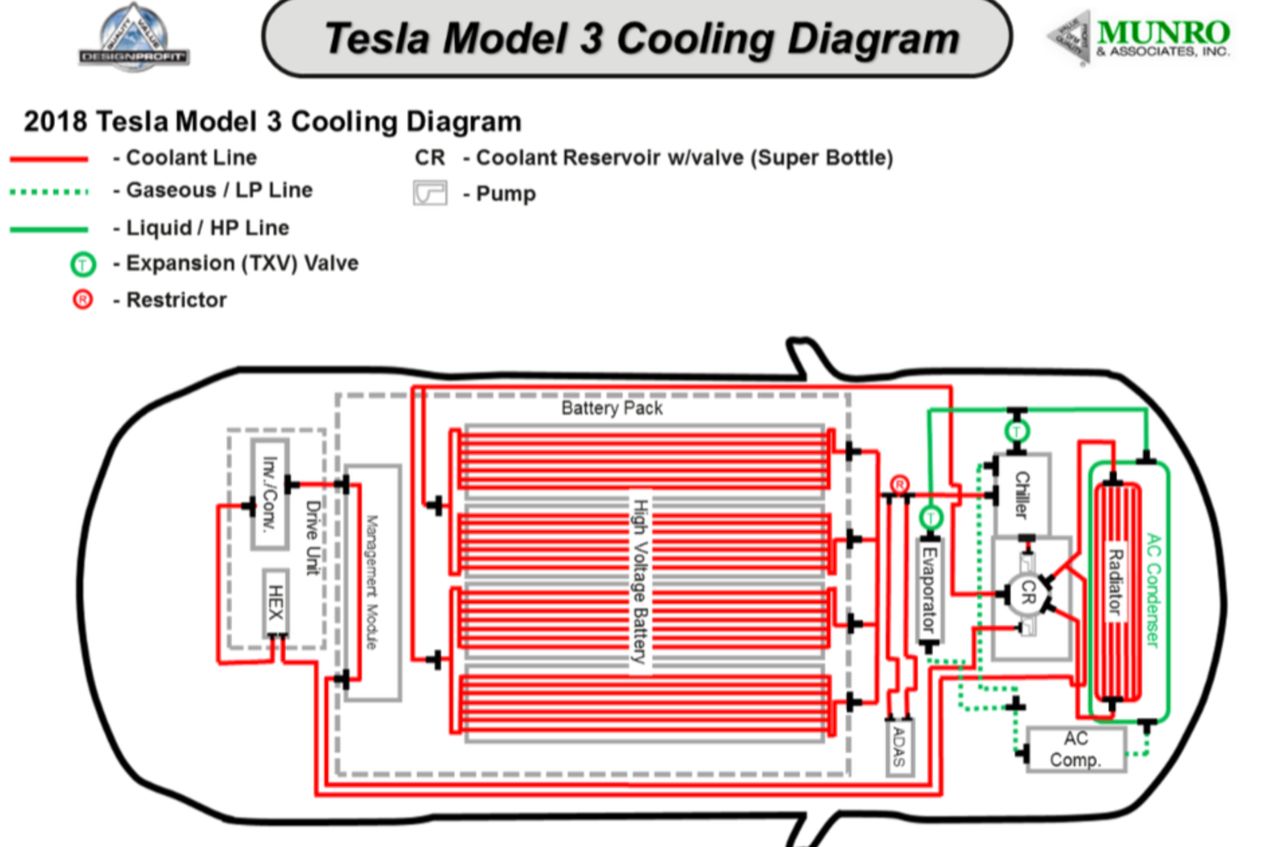
Performance management: The cooling system is a core component of an EV, often employing intelligent systems linked to navigation or predictive algorithms to optimize cooling efficiency (air versus liquid) based on conditions and driving scenarios to conserve energy.

Key components of an electric vehicle cooling system
Coolant: A mixture of water and ethylene or propylene glycol additives to prevent freezing, boiling, and corrosion.
Radiator: Transfers heat from the coolant to the outside air.
Pumps and valves: Circulate coolant and regulate flow between components.
Electric vehicle cooling system maintenance
Maintenance of the EV cooling system involves regular checks of coolant levels, inspecting hoses and radiators for leaks, keeping radiator fins clean, and flushing or replacing coolant according to usage intervals. Using the correct coolant specified by the manufacturer and updating software are essential to ensure proper thermal management and prevent battery overheating.
Maintenance
Regularly inspect radiators, hoses, and connectors for damage or leaks. Refill and replace coolant as per the manufacturer's recommended service intervals, and monitor coolant levels.
Clean radiator fins: Ensure radiator fins are free from dust or insect debris that could block airflow, improving cooling efficiency and air circulation.
Use manufacturer-specified EV coolant: Use the type of coolant recommended to prevent corrosion and avoid mixing different coolant types.
Monitor warning signs: Unusual noises, warning symbols such as radiator or turtle icons, strange odors, or poor acceleration may indicate cooling system issues, possibly due to battery or motor overheating.
Software updates are critical and should not be neglected: Regular software updates improve battery management and cooling performance.
Park in shaded areas: Parking in shade helps prevent battery overheating during extremely hot weather.