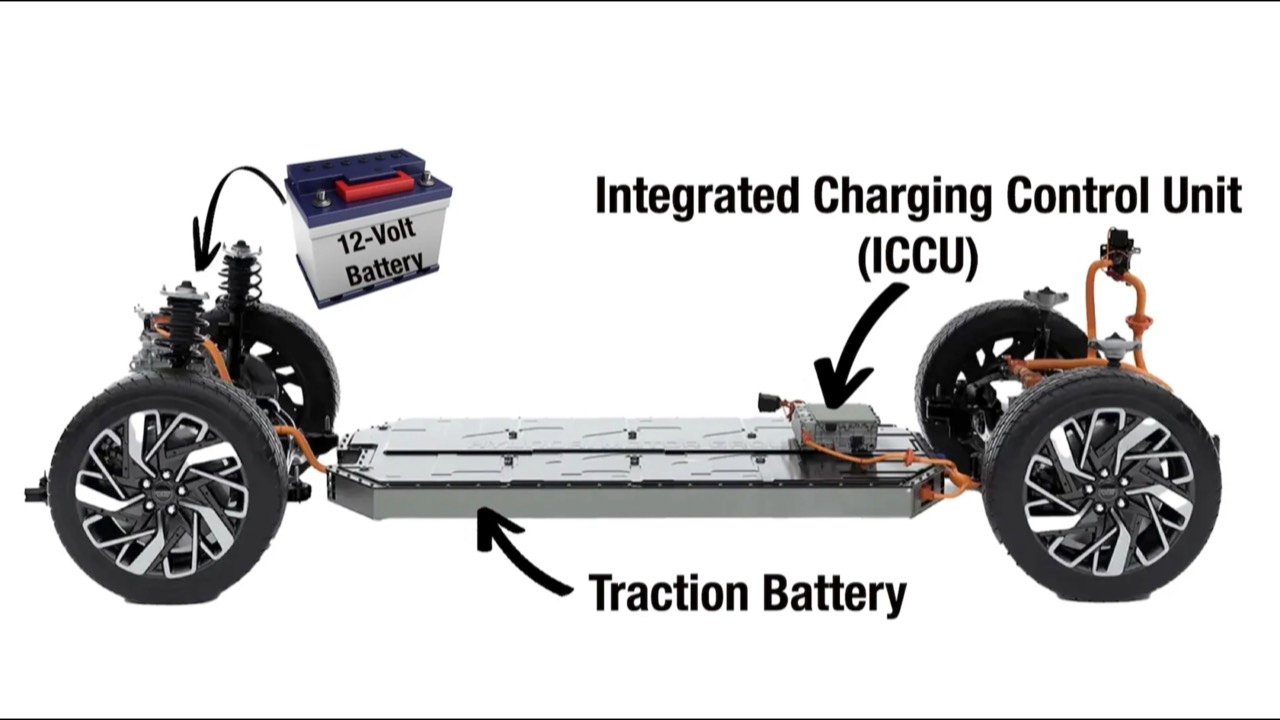
Although fully electric vehicles have a large main battery, many people think they have only that single battery. In fact, electric vehicles also have a 12-volt battery like those in gasoline-powered cars. This raises the question: why does a fully electric vehicle, which already has a large battery, also have a 12-volt battery? The answer lies in the various systems and components that make up the electric vehicle, as well as the distinct roles of the 12-volt battery.

What is the function of the 12-volt battery in electric vehicles?
In electric vehicles, the 12-volt battery has several important roles. Its primary function is to supply power to the vehicle's electrical systems when the car is not in use—such as the locking system, alarm, and other safety features. The 12-volt battery also powers the vehicle's computers and monitoring systems, and it starts the main high-voltage battery pack, which powers the electric motor and drives the vehicle. Another key role is acting as a buffer for the main high-voltage battery pack, helping to reduce power fluctuations from the high-voltage battery to ensure a steady electrical supply. There are several reasons why the high-voltage battery pack cannot directly supply continuous power to the vehicle's electrical systems instead of using a separate 12-volt battery.
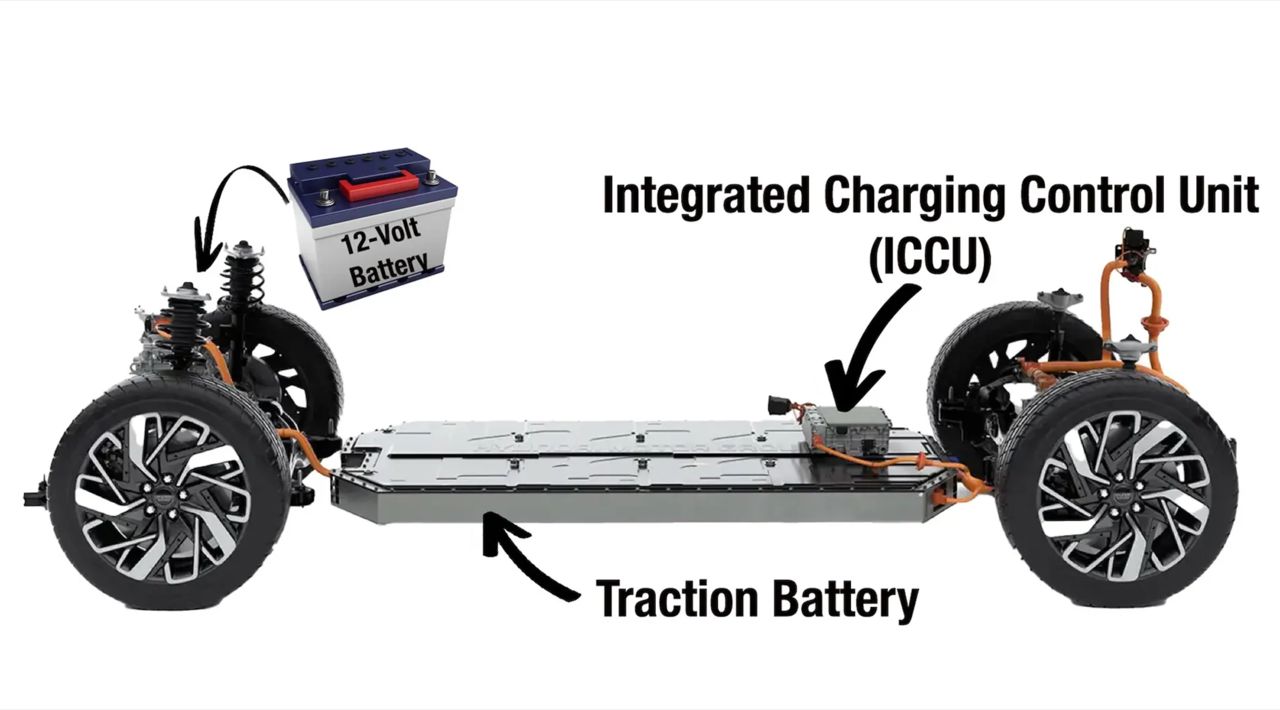
First, the main high-voltage battery pack is designed to supply power to the electric motor to drive the vehicle, not to provide a continuous electrical supply to the vehicle’s systems. Using the high-voltage battery to power all electrical systems would place a heavy burden on it and could reduce its overall lifespan.
Additionally, the main high-voltage battery pack is typically larger and heavier than the 12-volt battery, which would add unnecessary weight to the vehicle. Using a separate, smaller 12-volt battery reduces vehicle weight and improves the overall efficiency of the electrical power source.

How is the 12-volt battery in electric vehicles charged?
A common question is how the 12-volt battery is recharged if it does not power the electric motor. Generally, the 12-volt battery in electric vehicles is charged through a trickle charging process, which uses a small amount of electricity from the main high-voltage battery pack to maintain the 12-volt battery’s charge while the vehicle is in use.
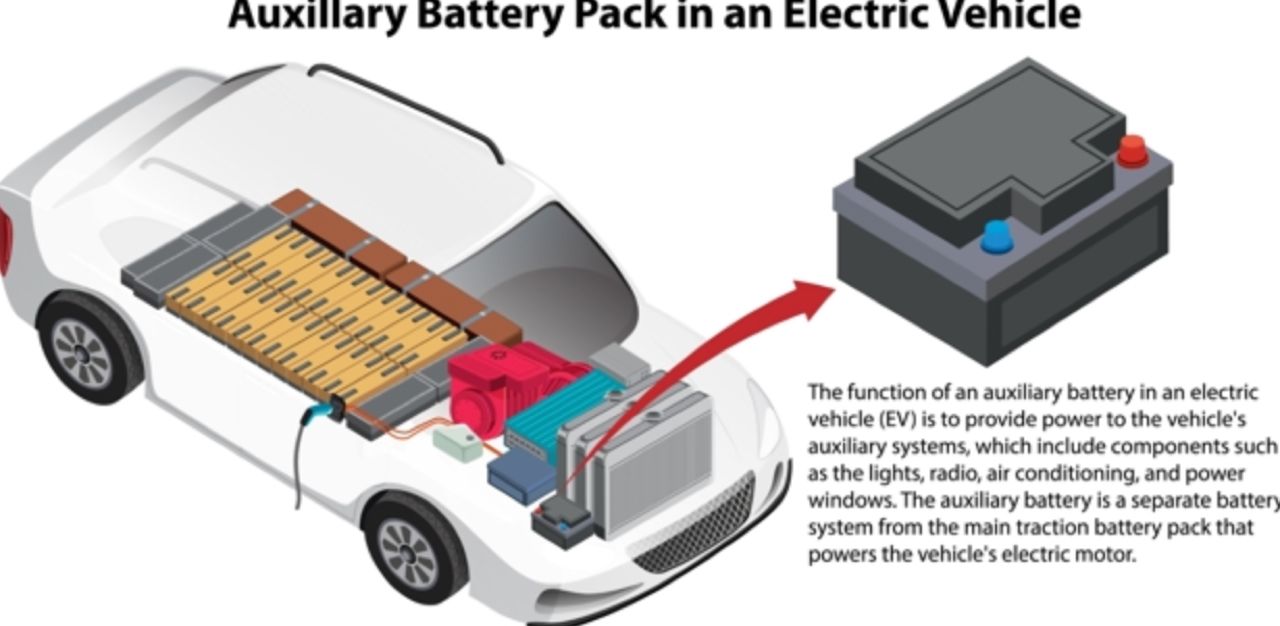
Trickle charging ensures that the 12-volt battery has enough energy to power small devices. Since the high-voltage battery primarily drives the vehicle, trickle charging also helps maintain battery health and extends its service life.
It is important to note that the 12-volt battery in electric vehicles differs from the 12-volt batteries found in combustion engine vehicles. The 12-volt battery in electric vehicles is a special type called a "deep cycle" battery, designed for regular discharge and recharge cycles. This contrasts with the "starter" batteries in gasoline cars, which provide short bursts of power to start the engine and are not intended for continuous discharge during driving.

What happens when the 12-volt battery in an electric vehicle runs out?
Like any car battery, the 12-volt battery in an electric vehicle will eventually need replacement. Sometimes it can fail suddenly, leaving the vehicle without power for electrical systems, especially problematic if it happens while driving.
If the 12-volt battery dies while the vehicle is in use, it may be possible to start the battery using another 12-volt power source, such as a portable jump starter. It is crucial to follow safety precautions when attempting to jump-start the battery due to the risk of electric shock. Extra caution is also necessary when working with electric vehicles because the high-voltage battery pack poses additional risks.
If the 12-volt battery cannot be started, the vehicle must be taken to a service center for battery replacement. In some cases, owners with the right tools and knowledge of the 12-volt battery specifications can replace it themselves, but it is generally safer and more reliable to have a trained technician perform this task.

Summary
Fully electric vehicles (EVs) still contain a 12-volt battery because it performs several critical functions.
The 12-volt battery in electric vehicles serves as the main power source for control systems and basic electrical devices such as lighting, infotainment screens, locks, and controlling the contactors that connect the high-voltage battery to the drivetrain. Without power from the 12-volt battery, the vehicle cannot start or operate.
Main functions of the 12-volt battery in electric vehicles:
Starting the vehicle (Wake-up system): It provides initial power to start the computers and electronic systems before the high-voltage battery comes online.
Safety system control: It powers headlights, taillights, turn signals, ABS brakes, and airbags.
Powering accessories: Interior lighting, power windows, power steering, and entertainment systems.
Activating contactors: It controls the opening and closing of the contactors that connect the high-voltage battery to the drivetrain. Without 12-volt power, the contactors cannot operate, and the vehicle will not drive.
Charging the 12-volt battery:
Electric vehicles do not have alternators but use a DC-to-DC converter to step down the voltage from the main battery (400-800 volts) to about 14 volts, continuously charging the 12-volt battery while the vehicle is in operation.