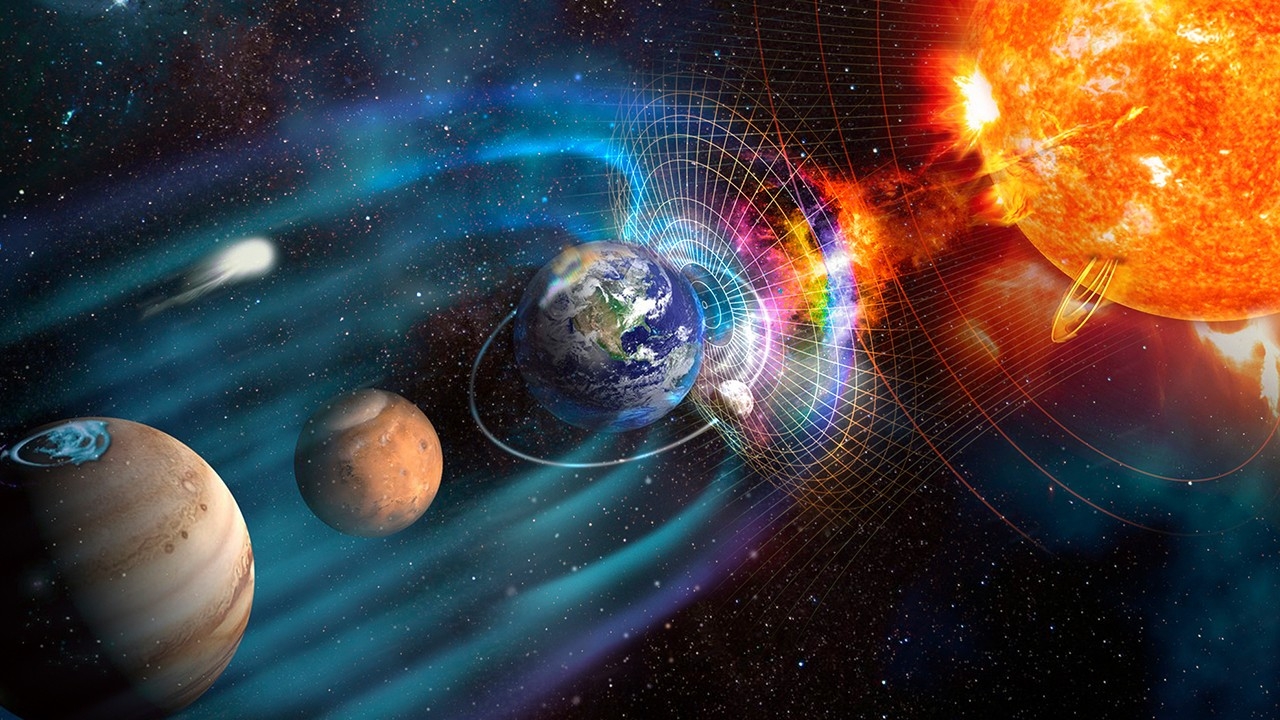

A geomagnetic storm is a condition where Earth's magnetic field becomes violently disturbed, primarily caused by solar activities such as Coronal Mass Ejections (CMEs) or high-speed solar winds that collide with Earth's atmosphere and magnetic field.
The Thai Astronomical Society posted a warning on 19 Jan 2026 stating that NOAA urgently announced a very strong G4-level geomagnetic storm warning for tomorrow (20 Jan 2026).
Regarding the effects of geomagnetic storms on Thailand, data shows the mechanisms by which geomagnetic storms impact Earth as follows.
When the Sun releases vast amounts of charged particles, these particles travel through space and disturb the Magnetosphere, Earth's magnetic shield, leading to the transfer of enormous energy into Earth's magnetic field system.
Impacts on Earth in various aspects.
Geomagnetic storms do not directly affect the human body (since the atmosphere filters out radiation) but significantly impact technology and infrastructure systems as follows:
Satellite systems and communications: High-energy radiation and particles can damage satellite solar panels or interfere with radio signals and GPS systems, causing location inaccuracies.
Power transmission systems: Geomagnetic storms can induce high electric currents (GIC) in long-distance power lines, potentially causing transformer explosions and widespread power outages.
Aviation: Aircraft flying near the poles may need to alter routes due to radio communication disruptions and to reduce radiation exposure for crew and passengers.
Auroras: A positive effect is the appearance of beautiful northern and southern lights visible at lower latitudes than usual.
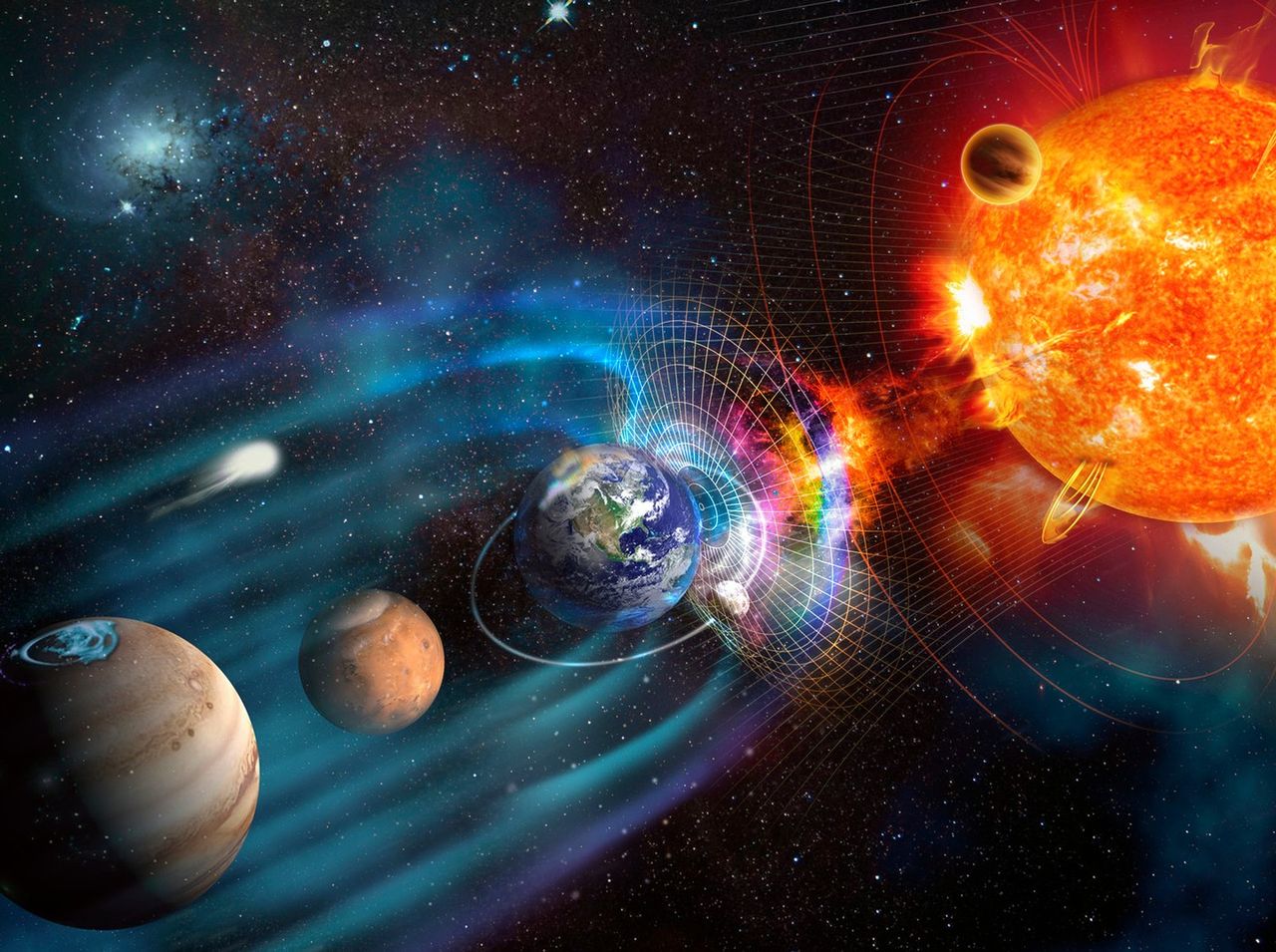
Examples of significant past events.
The Carrington Event (1859): The strongest recorded geomagnetic storm, which caused telegraph systems worldwide to fail and fires in some locations, with auroras reported as far as the equator.
The Quebec blackout (1989): A severe geomagnetic storm caused the power grid in Quebec, Canada, to collapse within minutes, leaving over 6 million people without electricity for more than 9 hours.
The May 2024 solar storm: The first maximum-level (G5) geomagnetic storm in over 20 years, producing auroras in previously unseen areas and affecting GPS systems and autonomous farming tractors in some regions.